

To contain and minimize the spread of infection, prompt and accurate diagnosis is of utmost importance to detect, isolate, treat, and trace infected individuals. Accurate detection of SARS-CoV-2 is however complicated by overlapping clinical symptoms such as fever, cough and sore throat that may be caused by other respiratory viruses. Similarly, other viral pathogens, such as arboviruses, are difficult to distinguish due to similar clinical presentations leading to poor disease management.
Traditional viral diagnostic methods, such as viral culture, immunofluorescence tests, and serological approaches, are time-consuming, labor-intensive, and have a high rate of cross-reactivity with other pathogens.
WHO has designated RT-PCR as the gold standard for detecting SARS-CoV-2 due to its great sensitivity and specificity in distinguishing viral pathogens. Despite its advantages, RT-PCR is extremely technical, costly, and difficult to use, making it unsuitable for point-of-care diagnostics, particularly in resource-limited situations. An innovative, fast, and simple approach for detecting viral pathogens infections is needed.
In light of this, the Centre for Health System Strengthening in collaboration with the Genomics and Infectious Disease Laboratory, KNUST with sponsorship from the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) are in the process of evaluating a PCR equipment, LOAA for the detection of arboviruses (Yellow fever, Dengue virus, Chikungunya, Zika virus) and respiratory viruses (RSV, SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza A and Influenza B)
 Initiation meetings and trainings at study sites
Initiation meetings and trainings at study sites
LOAA is a novel platform that makes use of nucleic acid amplification techniques to provide real time, qualitative detection of viral pathogens by aid of a dual labeled hydrolysis probe, TaqMan and target specific primers. LOAA has potential to be deployed as a point-of-care device that will provide a relatively simpler and faster approach to detect arboviruses and respiratory viruses.
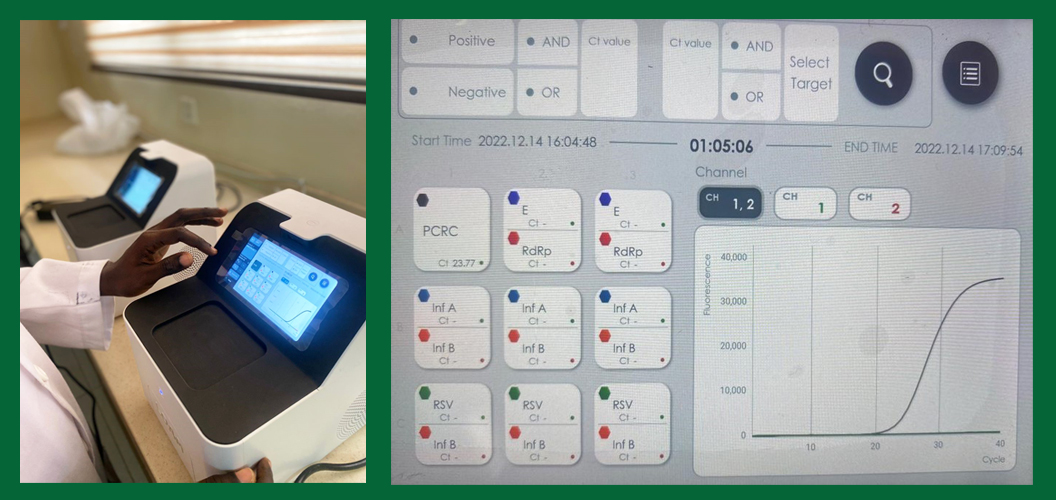 The LOAA machine
The LOAA machine
The sites for the study are the HopeXchange hospital, KNUST hospital and five selected facilities in the Savannah region.
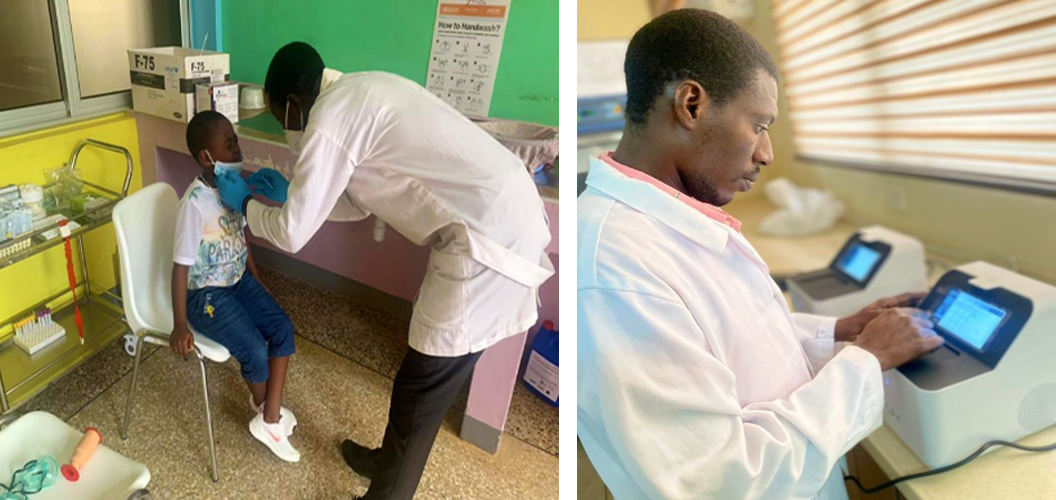 Sample collection and testing on the LOAA machine
Sample collection and testing on the LOAA machine 
